
The last part of the EEG test involves your child looking at a controlled flashing light. Later they will be asked to hyperventilate (do some deep breathing). Children old enough to cooperate will be asked to open and close their eyes during the recording. If no typical events are recorded, the video is deleted. This gives the neurologist an accurate visual record in conjunction with the EEG recording. A video is recorded in case an event occurs. After the electrodes have been placed, your child needs only to remain reasonably still while the scientist sits at the computer watching the screen. The scientist will clean these areas lightly with a cotton bud before placing the electrodes (usually 23 small metal discs) on the scalp, and keep them in place with a sticky paste (not glue) and some light tape. After explaining the procedure, the scientist will measure your child's head and mark the scalp with a soft pencil where electrodes will be placed. Your child will either sit in a reclining chair or be nursed by you. Before testing, the EEG scientist will ask a few questions about your child even though you may have given this information to your doctor. If your child has episodes during specific situations, such as during sleep, please speak to your doctor or our EEG staff about the implications for the EEG recording, as it may be possible to provoke these episodes. If your child has special needs or you think he/she may not be able to cooperate with the procedure, please contact our EEG staff to discuss your concerns and the best course of action. Younger children may benefit from dummies, bottles and other comforters. Distractions such as toys and DVDs are provided. The EEG technologist is experienced in helping children to relax. Toddlers may not enjoy the experience, much like a hair cut or hair wash. Ideally we need your child to be fairly still during the recording. Recent chicken pox must be completely healed in order for the EEG to occur. If your child has hair lice, please make a new appointment, as health precautions prevent us from carrying out an EEG on a child with lice. We need your child to have clean, dry hair with no extra products such as oil or gel.  help localise the site of seizure activity in a child with focal epilepsyĪn EEG can occasionally lead to confusion, especially if non-specific abnormalities or epileptic activity is seen in a child without seizures. monitor treatment in some types of epilepsy. help confirm or exclude epilepsy, following a thorough clinical evaluation (usually with EEG recording during episodes). help make a specific (syndrome) diagnosis in a child with epilepsy. help distinguish focal from generalised seizures and epilepsies. The main roles of EEG in the evaluation of children with epilepsy are to: The interpretation of EEG findings in children can be difficult and it is recommended that EEGs in children are recorded and interpreted by clinicians experienced in paediatric EEG. A normal EEG during a "seizure" usually excludes epilepsy as the cause.
help localise the site of seizure activity in a child with focal epilepsyĪn EEG can occasionally lead to confusion, especially if non-specific abnormalities or epileptic activity is seen in a child without seizures. monitor treatment in some types of epilepsy. help confirm or exclude epilepsy, following a thorough clinical evaluation (usually with EEG recording during episodes). help make a specific (syndrome) diagnosis in a child with epilepsy. help distinguish focal from generalised seizures and epilepsies. The main roles of EEG in the evaluation of children with epilepsy are to: The interpretation of EEG findings in children can be difficult and it is recommended that EEGs in children are recorded and interpreted by clinicians experienced in paediatric EEG. A normal EEG during a "seizure" usually excludes epilepsy as the cause. 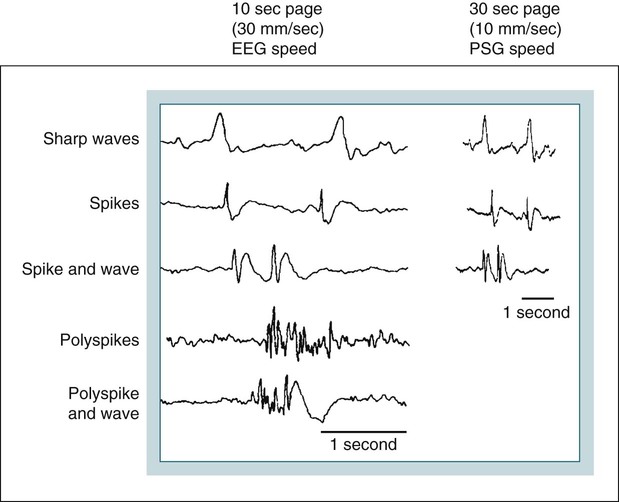
Many types of epilepsy may be associated with a normal EEG between seizures.

Furthermore, about 2% of normal school-age children who do not have seizures have epileptic activity on EEG.Ĭonversely, a normal EEG does not exclude epilepsy.

cerebral palsy, autism, speech delay) and do not mean that the child has epilepsy. Non-epileptic abnormalities and even epileptic activity may be recorded in children with neurological and behavioural problems (eg. Minor irregularities of no significance are frequently seen in EEG recordings of normal children, especially infants and young children. Focal abnormalities seen on an EEG occasionally warrant a child having a brain scan. Many types of childhood epilepsy have characteristic epileptic activity on the EEG that leads to a specific diagnosis and treatment. This epileptic activity can take several forms and be either generalised (recorded over all regions) or focal (recorded in one or more localised regions). In people with epilepsy, there may be "epileptic activity" on the EEG indicating their predisposition to seizures. The brain waves may be normal or show abnormalities in certain regions. The EEG recording shows rhythmical electrical activity, often called brain waves. This is recorded on a computer and interpreted by a neurologist What does the EEG show?
Some questions that your child might ask about an EEGĪn electroencephalogram (EEG) is a safe and pain-free test which records the electrical activity of the brain.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
